Enamel Hypoplasia: Causes, Treatment & Prevention
Every tooth has an external protective layer known as enamel. Enamel is an outer layer on the visible part of the crown of the tooth. It is the hardest and most highly mineralized substance of the body. It prevents bacteria from damaging the inner pulp of the teeth. The hard covering comes from the minerals such as calcium phosphate and hydroxy apatite which make enamel the hardest and most durable substance in your body
Enamel makes teeth smooth. The formation of enamel is very sensitive process, any disturbances that occur during the tooth development can result in enamel defects, affecting the primary or permanent teeth. The “6-year-old molars” (first permanent molars) are most prone to enamel defects.
Hypomineralisation (hypocalcification) and hypoplasia are the most common developmental dental defects. They both occur because of a disruption in the developmental process of the tooth, which occurs when a child is in utero or in the first few years of life.
Enamel hypomineralisation is known as ‘Chalky Teeth’ .It develops, where enamel is less mineralized (reduced thickness) or of poor quality.
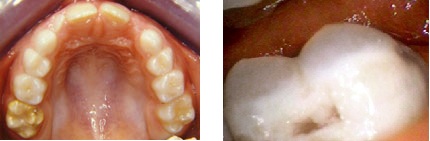 Chalky teeth
Chalky teeth
Hypomineralization of a tooth occurs when the enamel of a tooth hasn’t mineralized as much as a healthy tooth.
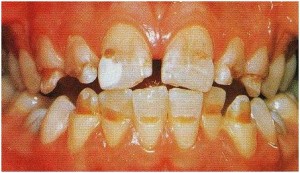
Normal enamel is a whitish and very hard. Hypomineralized enamel is more porous, look mottled, with opaque whiteness or creamy white, yellow, or brown color spots and is chalky in texture. As a result these teeth look unattractive and more susceptible to breaking, wearing down or decay at much faster rates because the teeth are so weak. Chalky teeth have the tendency to break down whether they are affected by decay or not.
Enamel is the hard protective layer of the tooth and when it is damaged the tooth is more prone to sensitivity and decay This is because the texture of hypomineralized enamel is often rough and can catch food, bacteria or plaque more easily. Additionally the affected teeth are more susceptible to wear because they are less resilient to chewing forces and dietary acids.
The child affected, may suffer sensitivity (dental pain) from hot or cold foods and drinks or tooth brushing. This varies from a minor inconvenience to daily disruption.
Enamel defects are one of many conditions that dentists in Delhi screen for in children’s routine checkup and clean appointments.
Hypocalcification is not decalcification, yet both are sometimes called a chalky or white spot.
Hypocalcification, or chalky spot, is a defect in the enamel of a tooth, either baby tooth or permanent tooth, caused by an insufficient amount of the normal minerals that make up tooth enamel. This causes the chalky spot.
Hypocalcification should not be confused with decalcification. As was said before, hypocalcification is an insufficient amount of the normal minerals that make up enamel.
Decalcification is the beginning of the decay process. The enamel may have been completely sufficient at one time but then demineralization resulted in decay.
The decalcification may begin on a good area of enamel on the tooth, but is more likely to begin on a hypocalcified (soft or chalky spot) area. Decalcification is actually the destruction of an area of tooth by constant bathing in acid. There are many causes of decalcification such as medicine, dry mouth, acidic foods and drinks, fluorosis, bacterial plaque, and even acid reflux.
Also, hypocalcification should not be confused with hypoplasia.
Enamel hypoplasia refers to surface pits and grooves in the teeth that occur because of a decreased quantity of enamel produced. Enamel hypoplasia means that a tooth or teeth have less enamel than is normal. The enamel that the teeth do have is hard and healthy, but there is not enough of it to fully protect the teeth.
This situation may occur as a result of an injury to, or a large cavity in the primary tooth. When the permanent tooth comes into the mouth, it may have a roughened, irregular, or pitted area in the enamel, corresponding to the defect.
Although quite different to enamel hypomineralisation, the conditions tend to get confused because of similarities in their technical names.
Children are being counseled about enamel defects and their treatment, routinely by dentists in Delhi.
What causes enamel defects?
There are many different risk factors have been linked to enamel defects in primary and permanent teeth in children. The most common risk factors include:
- Mother’s health during pregnancy (illnesses, diet deficiency)
- Prematurity
- Birth difficulties
- Medications given to mother prior birth or to child during early childhood
- Early childhood diseases (high fever, pneumonia, middle ear infection, tonsillitis viral infections etc.)
- Chronic / frequent childhood illness during first four years of life
- Poor childhood nutrition
- Trauma to mouth or primary teeth can cause localised enamel defects
Rarely, enamel defect can be inherited and is called Amelogenesis Imperfecta. Every primary and permanent tooth has abnormal enamel formation.
Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) is the most severe type of enamel defect and is quite rare. It is a genetic disorder where the enamel of all of the teeth is affected. There are many different types of AI dependent on the genes affected. These types vary in severity from decreased mineral content of the enamel to total lack of enamel present.
What are the dental problems as a result of enamel defects?
- Affected teeth can be fragile and may wear or lose enamel easily
- Increase risk of dental decay
- Tooth sensitivity from hot and cold foods and drinks if the underlying dentine layer is exposed
- Socially, child may feel embarrassed to smile
Management and treatment
Essentially, they are very difficult to treat. If we can identify this condition early then we can monitor it for severity and manage it accordingly, before pain and tooth loss.
Management of hypomineralisation focuses on preventing decay (as soft areas can lead to rapid tooth decay) and controlling sensitivity.
Other times, the problem may be slight and be more of a cosmetic concern than a dental health problem.
We certainly do our best to ensure our younger patients don’t associate the dentist with pain, but this condition will make their teeth hyper-sensitive. This means it is very difficult to numb the teeth in order to treat them.
Depending on the situation we have been able to put crowns on these teeth. However if we see them late then often the teeth are so damaged there is no choice but to extract them.
If the incisor teeth are affected it may be of an aesthetic concern, and there are a variety of treatments available to restore a healthy happy smile.
If the spots only affect tooth appearance, the dentist may suggest bleaching, which can improve the appearance of the spots. However, if the discoloration is persistent, the dark-colored areas can be removed and filled.
Also, they are very hard to fill because the materials that are used for fillings are designed to adhere to enamel that is healthy and has minerals in it. Without the proper amount of mineral, then the fillings just don’t stick and the tooth just continues to break.
In mild scenarios affecting the molar teeth, fissure sealants can be placed to protect the weak enamel from decay. However in more severe cases the enamel may be too damaged for any type of restoration to adhere to, or the volume of the tooth affected may be too large to be treated with a conventional fissure sealant or filling. Pit and fissure sealants in children’s teeth are a routine procedure in dental clinics in India.
If the soft areas are smaller, fillings can be effective, but they may need to be replaced later. After the teeth have grown, a permanent cap or crown can help prevent further decay into adulthood.
In the case of soft or thin enamel, your dentist may decide to act sooner. Soft or ill shaped teeth can make teeth cleaning at home more difficult. If the quality of the enamel is only slightly affected, your dentist may suggest
- limiting acidic foods and sugary treats, especially those that dissolve enamel. Candies like suckers and drinks like sodas should be a very rare part of your child’s diet.
- a strict brushing and flossing routine, as misshapen teeth can be harder to clean.
- a diet rich in calcium, including leafy greens. When the body is deficient in calcium, it will start to break down calcium stored in the teeth, which can further weaken the enamel.
If we can identlfy this condition early then we can possibly use crowns or stainless steel pediatric crowns to protect the affected teeth from decay and to allow the child to eat, drink and brush their teeth without pain until all the child’s teeth have fully erupted. Dentists in India are focusing more on the health of children’s teeth.
In severe cases of hypomineralisation, your dentist may advise to extract the severely affected teeth. The philosophy behind this is to avoid exposing the child to a lifetime of repetitive dental care for these teeth. Additionally, removing the affected teeth may be beneficial if the child already has crowding of their teeth. If the affected six-year-old molars are removed in time, the 12-year-old molars still developing in the bone can grow forward into the space left behind. The wisdom teeth may then be able to fully grow into the jaw, so the child will still have two adult molar teeth.
Enamel defects in adults are being treated routinely by smile makeover procedures in reputed dental clinics in Delhi.
Posted By – Dr. Shriya